SeaTable cluster¶
This instruction needs rework
This documentation is out of date. We will update the documentation shortly.
SeaTable Enterprise Edition support cluster for high availability and better performance.
A general architecture is like following:
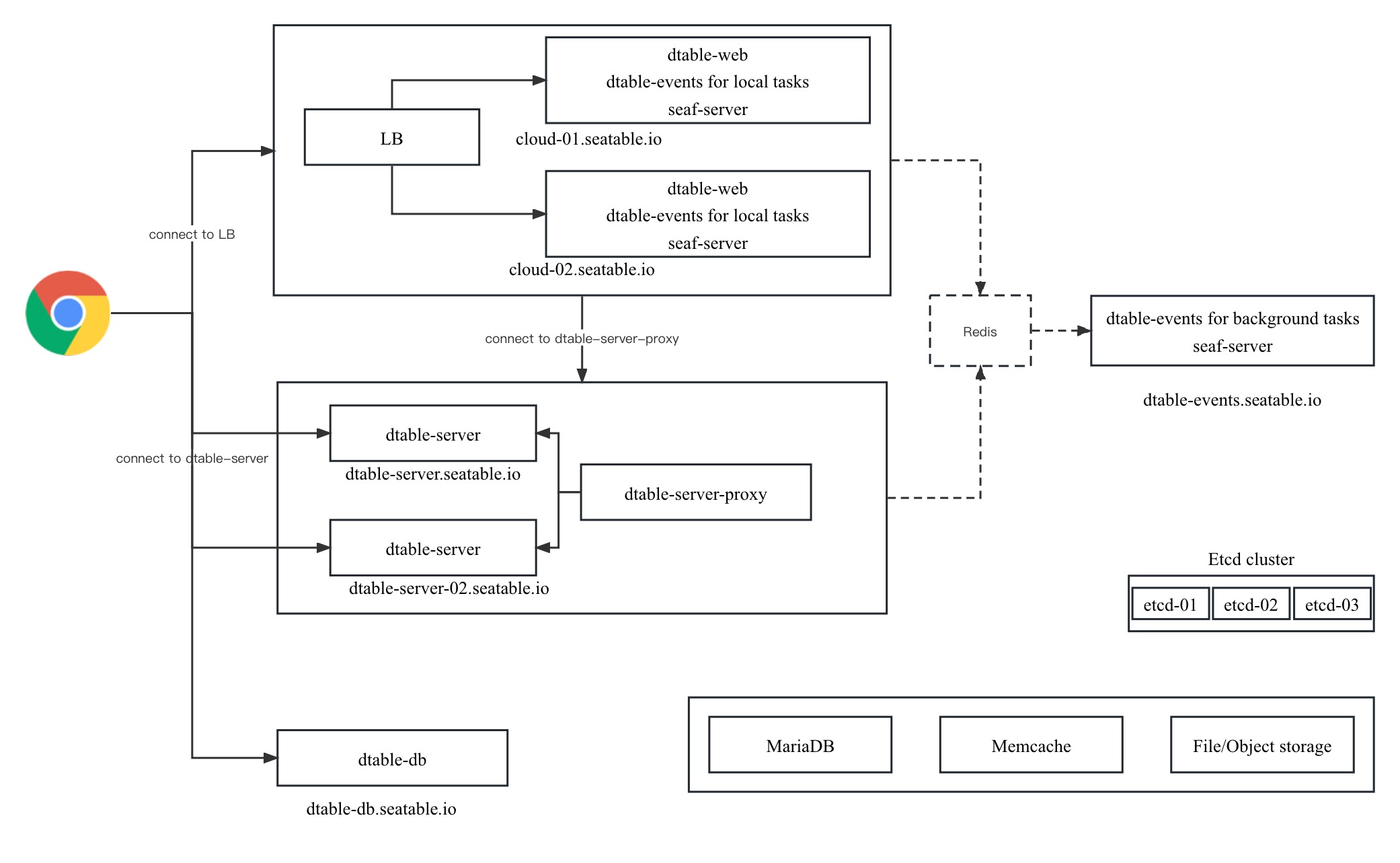
All nodes use the same docker image, with a different docker compose file and seatable-controller.conf to control the behavior.
There are five external service needed for the cluster:
- MariaDB/MySQL service
- Redis, used as a way to pass event from one component to others
- Memcached
- Object storage
- Etcd, a reliable key-value storage to store information about which base assigned to which dtable-server
The cluster consistents of the following components:
- Several dtable-web nodes behind a load balance
- Several dtable-server nodes, each with its domain, need to be accessed via the clients (browsers) via websockets directly
- A dtable-db node, as dtable-db has a high performance, there is no need to have several dtable-db nodes yet.
- A background dtable-events node for background tasks, like sending emails.
There is also a dtable-server proxy node which provide API access to dtable-servers for other components. So that other components don't need to know there are several dtable-servers, and don't need to know which base is assigned to which dtable-server.
Note, to improve performance of your SeaTable service, you don't need to setup a full cluster. Sometimes, use a standalone dtable-server can help improve performance. In the following manual, we will show the steps to setup a two nodes deployment:
- A dtable-web node running dtable-web, seaf-server, dtable-events, dtable-db and dtable-storage-server
- A dtable-server node running dtable-server, dtable-storage-server
Note, dtable-storage-server provide access to the underlying object storage system, so it need to be run at each nodes.
Setup dtable-web nodes¶
First, setup a one node deployment according to Enterprise-Edition
Then, use storage backend according to S3 Object Storage
Modify configuration file¶
Modify docker-compose.yml to let Redis can be accessed from another node
redis:
image: redis:5.0.7
container_name: seatable-redis
ports:
"192.xx.xx.xx:6379:6379" # dtable-web server's IP
Modify dtable-web configuration file /Your SeaTable data volume/seatable/conf/dtable_web_settings.py
USE_INNER_DTABLE_SERVER = False
DTABLE_SERVER_URL = 'https://dtable-server.example.com/' # dtable-server's url
DTABLE_SOCKET_URL = 'https://dtable-server.example.com/' # dtable-server's url
Modify dtable-db configuration file /Your SeaTable data volume/seatable/conf/dtable-db.comf
[dtable cache]
private_key = "xxx"
dtable_server_url = "https://dtable-server.example.com/"
total_cache_size = 100
Create configuration file : /Your SeaTable data volume/seatable/conf/seatable-controller.conf
ENABLE_SEAFILE_SERVER=true
ENABLE_DTABLE_WEB=true
ENABLE_DTABLE_SERVER=false
ENABLE_DTABLE_DB=true
ENABLE_DTABLE_STORAGE_SERVER=true
ENABLE_DTABLE_EVENTS=true
DTABLE_EVENTS_TASK_MODE=all
DTABLE_EVENTS_TASK_MODE can be all, foreground, background. Here we use all. If you want to deploy a separate background node for running dtable-events, use foreground here.
Restart dtable-web server¶
docker compose up -d
docker exec -it seatable bash
seatable.sh
When you see following in the output log, it means success:
Skip dtable-server
SeaTable started
Setup dtable-server¶
Copy and modify docker-compose.yml¶
The default directory for SeaTable is /opt/seatable. Create the directory:
mkdir /opt/seatable
Copy the docker-compose.yml file on the dtable-web server and modify docker-compose.yml.
vim /opt/seatable/docker-compose.yml
services:
seatable:
image: seatable/seatable-enterprise:latest
container_name: seatable
ports:
- "80:80"
- "443:443" # If https is enabled, cancel the comment.
volumes:
- /opt/seatable/shared:/shared # Requested, specifies the path to Seafile data persistent store.
environment:
- SEATABLE_SERVER_HOSTNAME=dtable-server.example.com # Specifies your host name if https is enabled
- SEATABLE_SERVER_LETSENCRYPT=True
- TIME_ZONE=Asia/Shanghai # Optional, default is UTC. Should be uncomment and set to your local time zone.
networks:
- dtable-net
networks:
dtable-net:
Copy and modify configuration file¶
Prepare configuration file directory
mkdir -p /opt/seatable/shared/seatable/conf
Copy the configuration file on the dtable-web server to the conf directory.
Modify the dtable-server configuration file : /Your SeaTable data volume/seatable/conf/dtable_server_config.json
{
"host": "mysql host",
"user": "mysql uer",
"password": "password",
"database": "dtable_db",
"port": 3306,
"private_key": "xxx",
"dtable_web_service_url": "xxx", # dtable-web server's URL
"redis_host": "192.xx.xx.xx", # dtable-web server's IP
"redis_port": 6379,
"redis_password": ""
}
Modify the Nginx configuration file : /Your SeaTable data volume/seatable/conf/nginx.conf
log_format your_log_format '[$time_iso8601] $http_x_forwarded_for $remote_addr "$request" $status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" "$http_user_agent" $upstream_response_time';
upstream dtable_servers {
server 127.0.0.1:5000;
keepalive 15;
}
server {
if ($host = dtable-server.example.com) {
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
listen 80;
server_name dtable-server.example.com;
return 404;
}
# This part of the configuration is for communication among nodes within the cluster.
server {
server_name 172.xx.xx.xx;
listen 80;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
location / {
if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS') {
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin *;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Methods GET,POST,PUT,DELETE,OPTIONS;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Headers "deviceType,token, authorization, content-type";
return 204;
}
proxy_pass http://dtable_servers;
...
access_log /path/to/dtable-server-inner.access.log your_log_format;
error_log /path/to/dtable-server-inner.error.log your_log_format;
}
}
server {
server_name dtable-server.example.com;
listen 443 ssl;
ssl_certificate /shared/ssl/<your-ssl.cer>;
ssl_certificate_key /shared/ssl/<your-ssl.key>;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
location /socket.io {
proxy_pass http://dtable_servers;
...
access_log /path/to/socket-io.access.log your_log_format;
error_log /path/to/socket-io.error.log your_log_format;
}
location / {
if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS') {
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin *;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Methods GET,POST,PUT,DELETE,OPTIONS;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Headers "deviceType,token, authorization, content-type";
return 204;
}
proxy_pass http://dtable_servers;
...
access_log /path/to/dtable-server.access.log your_log_format;
error_log /path/to/dtable-server.error.log your_log_format;
}
}
Create configuration file : /Your SeaTable data volume/seatable/conf/seatable-controller.conf
ENABLE_SEAFILE_SERVER=false
ENABLE_DTABLE_WEB=false
ENABLE_DTABLE_SERVER=true
ENABLE_DTABLE_DB=false
ENABLE_DTABLE_STORAGE_SERVER=true
ENABLE_DTABLE_EVENTS=false
DTABLE_EVENTS_TASK_MODE=all
Start dtable-server¶
docker compose up -d
docker exec -it seatable bash
seatable.sh
When you see following in the output log, it means success:
Skip seafile-server
Skip dtable-events
Skip dtable-web
Skip dtable-db
SeaTable started